Watering hole phishing is one of the more sophisticated cyberattack strategies used by threat actors today. It leverages the trust users have in frequently visited websites to deliver malware and steal sensitive information. In this guide, we’ll explain what watering hole phishing is, how attackers execute these scams, how you can spot them, and the best measures to protect yourself online.
What Is Watering Hole Phishing?
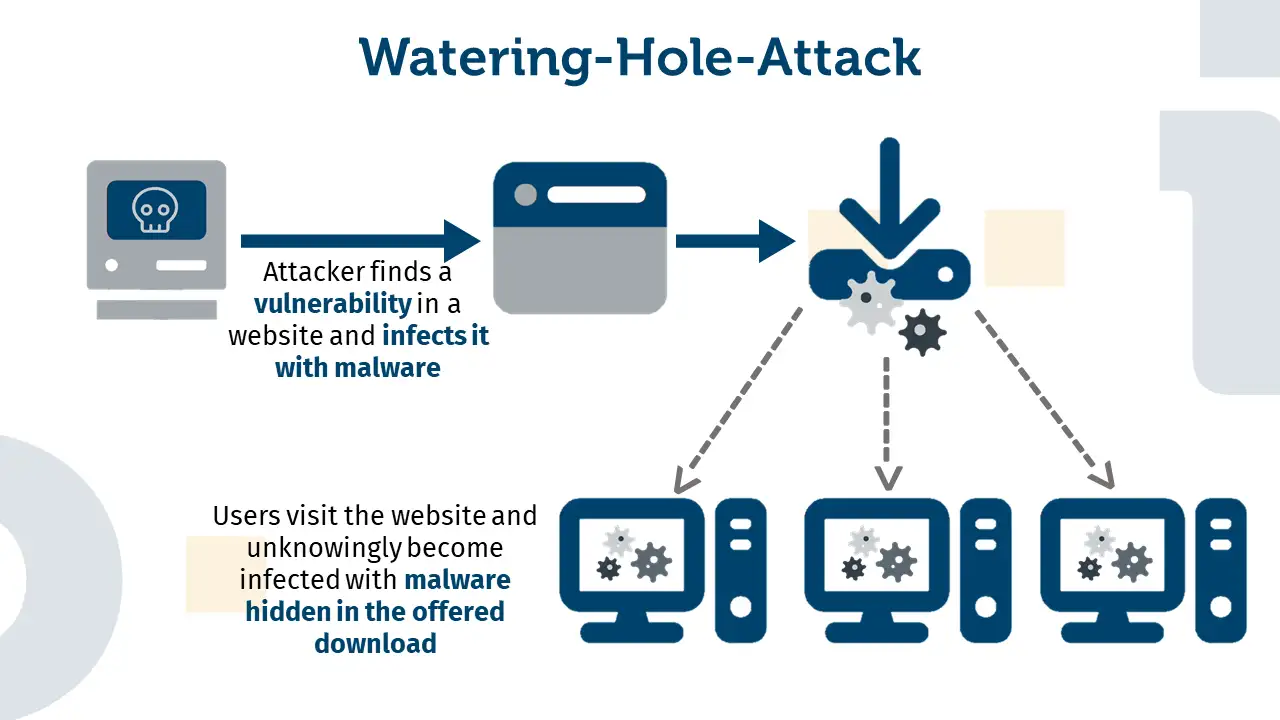
Watering hole phishing is a targeted attack in which cybercriminals compromise a website or online resource that a particular group or organization frequently visits. The term is derived from the natural behavior of predators waiting at watering holes for prey to come and drink. In the digital world, attackers “lurk” on trusted sites, infect them with malicious code, and then wait for users to visit—often without any obvious signs of danger.
Key Characteristics:
- Targeted Websites: Instead of sending mass phishing emails, attackers identify websites that members of a specific community or organization use regularly.
- Infection Through Vulnerabilities: Attackers exploit zero-day or known vulnerabilities in the site’s software or plugins to inject malware.
- Stealth Delivery: Since the site is usually legitimate and trusted, users rarely suspect that their visit could result in a compromise.
How Do Watering Hole Phishing Attacks Work?
Watering hole attacks generally follow a multi-step process:
- Reconnaissance:
Attackers research the target group to determine which websites they visit most frequently. They gather intelligence through social media, online forums, and browsing patterns. - Website Compromise:
Using vulnerabilities—often in outdated software or plugins—cybercriminals inject malicious code into the targeted website. This code may be designed to download malware automatically or redirect the user to a phishing page. - Infection:
When a user visits the compromised site, the malicious code executes in the background. The user’s device is silently infected, often without any visible signs of trouble. - Data Exfiltration:
Once inside, attackers can steal sensitive data, capture login credentials, or even gain remote control over the victim’s device or network.
How to Spot a Watering Hole Phishing Scam
While watering hole attacks are particularly insidious due to the trusted nature of the compromised site, there are warning signs and techniques you can use to detect potential threats:
- Browser Warnings:
Modern browsers and antivirus software may alert you if a site is flagged for suspicious activity or if there is a problem with its security certificate. - Unusual Website Behavior:
If a trusted site suddenly displays unexpected pop-ups, redirects you to unfamiliar pages, or starts auto-downloading files, it could be compromised. - Certificate and URL Checks:
Always inspect the URL and security certificate (look for “HTTPS” and the padlock icon) before entering sensitive information. Even small discrepancies can indicate foul play. - Abnormal Performance:
A sudden slowdown in your browser or unexpected network activity may be a sign that your device is communicating with a malicious server. - Reports and Alerts:
Stay informed about any security alerts or advisories from reputable sources regarding popular websites. Often, cybersecurity firms or news outlets will report if a frequently visited site has been compromised.
Essential Measures to Protect Yourself
Preventing watering hole phishing requires a multi-layered approach, combining software security, safe browsing practices, and regular updates. Here are some key measures you can take:
1. Keep Your Software Updated
- Regular Patching:
Ensure that your operating system, browsers, and any plugins (such as Flash or Adobe Reader) are always up to date. Patches often address vulnerabilities that attackers exploit. - Auto-Updates:
Enable automatic updates where possible to reduce the risk of missing critical security fixes.
2. Use Robust Security Software
- Antivirus & Anti-Malware:
Install reputable antivirus and anti-malware software that can detect and neutralize threats before they cause harm. - Firewalls & Intrusion Detection:
Utilize firewalls and network intrusion detection systems (IDS) to monitor and block suspicious activity.
3. Practice Safe Browsing
- Verify Websites:
Type website URLs manually or use trusted bookmarks instead of clicking on links from unsolicited emails. - Avoid Public Wi-Fi:
Be cautious when accessing sensitive information on public Wi-Fi networks. Use a virtual private network (VPN) to encrypt your connection. - Educate Yourself:
Familiarize yourself with common cyberattack techniques and red flags. Awareness is a powerful tool in preventing phishing scams.
4. Enhance Browser Security
- Browser Extensions:
Consider installing security-focused browser extensions that block malicious scripts and warn about compromised websites. - Disable Unnecessary Features:
Turn off features like Flash or JavaScript on websites where they aren’t needed, as these can be common targets for attackers.
5. Monitor Your Network Activity
- Regular Scans:
Periodically scan your device for malware and unusual network activity. - Alert Systems:
Set up notifications for any suspicious login attempts or unauthorized changes to your system settings.
6. Use Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
- Extra Verification:
Enable MFA on your online accounts. This adds an additional layer of security, making it more difficult for attackers to access your accounts even if they steal your credentials.
Conclusion
Watering hole phishing exploits the very trust you place in your favorite websites. By understanding how these attacks work, knowing the red flags, and taking proactive security measures, you can greatly reduce your risk of falling victim to this sophisticated scam. Staying updated, using robust security tools, and practicing safe browsing habits are all critical components in your defense against watering hole phishing.
By incorporating these strategies, you’ll not only protect your personal data but also contribute to a safer online community.
For more detailed insights on cybersecurity and to stay informed about the latest threats, subscribe to our newsletter and follow our blog.